AI in Investment: Ally or Adversary?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a transformative force reshaping the world, and the investment sector is not immune to its influence. AI’s utility extends beyond conceiving innovative products and services; it enhances existing enterprises and stimulates the creation of novel industries. PricewaterhouseCoopers predicts a $15.7tn contribution to the global economy from the AI market by 2030.
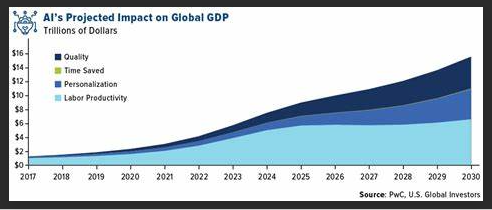
The investment opportunities envisaged can be distilled into three main categories:
- AI Development: Visionaries like OpenAI, Alphabet’s DeepMind, and a myriad of AI-focused startups are driving new technology, product, and service creation.
- AI Applications: Firms integrating AI into their operational mechanisms, ranging from tech giants such as Google and Amazon to budding startups reshaping industries like pharmaceuticals and logistics, offer compelling investment potential.
- AI Infrastructure: The successful implementation of AI hinges on robust infrastructures like cloud computing and data centres. Hence, businesses offering these indispensable services could be rewarding investment prospects.
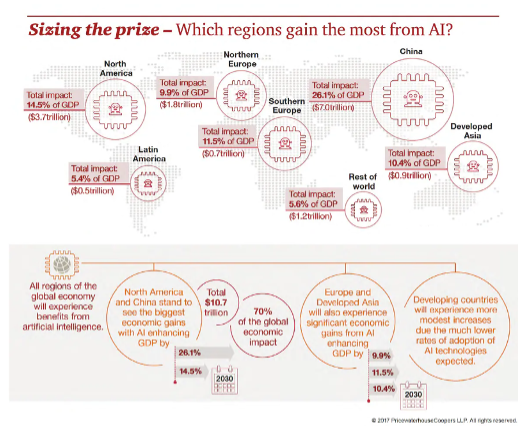
Consequently, the AI domain presents diverse investment opportunities, including:
- Investment in AI companies pioneering new products and services.
- Investment in firms leveraging AI to enhance their existing operations.
- Investment in entities generating unique industries rooted in AI.
However, the AI-driven investment arena is not devoid of risks, encompassing:
- Scams: AI’s potential for deception includes the creation of fake news, deepfakes, and other duplicitous entities. For instance, a convincingly fabricated video featuring Martin Lewis, the founder of MoneySaving Expert, recently circulated on social media. The AI-produced scam video mimicked Lewis’s likeness and voice to falsely endorse an app tied to Tesla and Twitter owner Elon Musk.
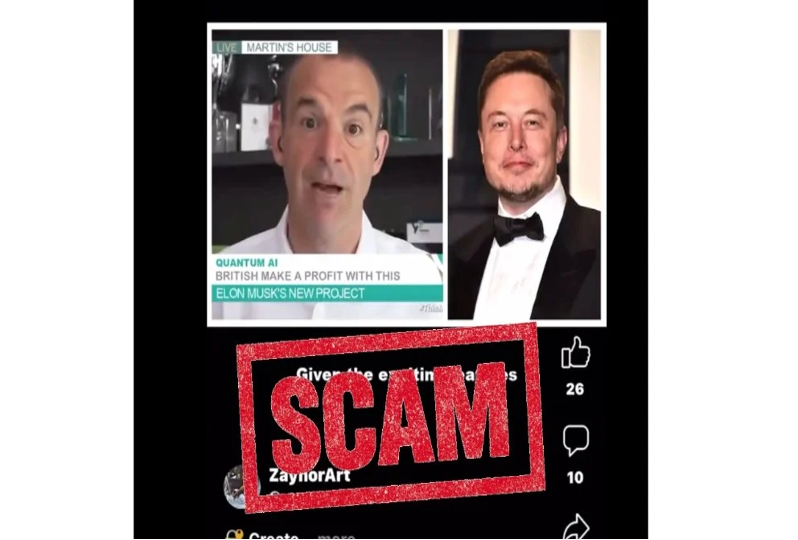
Despite its role as an innovation harbinger, AI introduces an array of challenges. The advent of ‘deepfakes’, AI tools adept at fabricating highly realistic audio and video, could spawn extensive disruptions and deceit. Moreover, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are exploited to execute complex scams, duping individuals into revealing sensitive data, resulting in considerable personal and financial fallout.
- Environmental Impact: Advanced AI models require massive computational power, leading to high energy consumption. A study by the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, exposed the environmental repercussions of AI, with a single AI model’s training equating to the lifetime emissions of five cars – around 300,000 kg of carbon dioxide.
- Trust and Ethics: AI’s ethical use mandates improved regulatory oversight and legal frameworks. Transparency in AI systems’ decision-making processes, along with education on AI technologies, their misuse potential, and preventive measures are crucial.
Social Concerns: AI’s growth stokes fears of job displacement and impacts democracy and politics. AI’s ability to automate tasks raises the spectre of job obsolescence, and inherent biases in AI data may perpetuate discriminatory practices. AI also runs the risk of inadvertently perpetuating inherent biases in the data it feeds on, potentially leading to discriminatory practices in critical areas such as recruitment, credit scoring, and judicial decision-making.
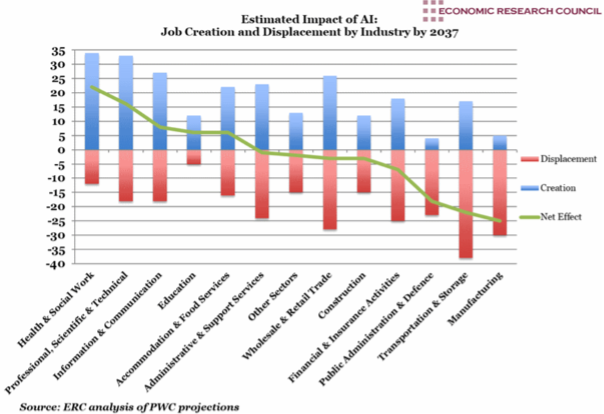
- Democracy: AI’s increasing role in influencing democratic processes, paired with the burgeoning presence of Big Data Analytics and the Internet of Things, threatens privacy and autonomy. It is commonly cited that interference by Russia and voter manipulation by Cambridge Analytica influenced both the 2016 American presidential election and the UK Brexit vote.
Without regulation AI will curate public discourse, our core values and democratic institutions.
- Governance: The task of regulating the swiftly evolving AI sector poses a considerable challenge to governments worldwide, given the transnational nature and diverse applications of AI.
- Data privacy: AI’s heavy data dependence imposes the responsibility of privacy rights protection on governments while harnessing AI’s potential. AI’s pervasiveness in society calls for a collective response to its challenges. Developers, users, governments, and the wider society must collaborate to ensure AI contributes to the common good rather than exacerbating societal issues.
Recommendations for Investors concerned about the impact of AI
- Conduct independent research: Understand the risks before investing in an AI firm.
- Invest in ethical companies: Firms committed to ethical AI practices are less likely to engage in scams or harm the environment.
- Invest in environment-friendly firms: Companies using AI to address environmental challenges are creating a more sustainable world.
In conclusion, AI, like many technological breakthroughs, presents a dual-nature – an invaluable ally offering unmatched innovation and investment possibilities and a potential adversary due to misuse risks. Navigating this landscape responsibly, with transparency and proper regulation, may allow us to restore trust and optimally benefit from AI’s exponential growth.








Comments (0)
To contact us please email enquiries@scmdirect.com.